Residential Segregation and Unequal Access to Local Public Services in India: Evidence from 1.5m Neighborhoods | A Study by Sam Asher, Kritarth Jha, Paul Novosad, Anjali Adukia, Brandon Tan
Policy makers who can only observe the world at an aggregate scale may fail to allocate public services fairly across neighborhoods, and may not even observe when misallocation takes place.
A group of Economists and Academicians have conducted a study on residential segregation and access to public services in 1.5 million rural and urban neighbourhoods for Muslims and Scheduled Castes (SC). The findings from the five-year project have substantiated the disparity in access to public services, such as primary and secondary schools, health clinics, drainage systems, and water and electricity infrastructure, between non-marginalized neighbourhoods and segregated SC or Muslim neighbourhoods. As per findings from the research, nearly 26% of Muslims and 17% of Scheduled Caste live in predominantly community-specific neighbourhoods, with over 80% of inhabitants belonging to their respective communities.
The study was driven by the number of marginalized groups in India (the studied marginalized groups constituted 300 million persons at the time of the research), the existence of disparity due to historical inequalities and the role played by market liberalization and urbanization in improving the situation, and the macro-level focus of Indian policy and planning.
…the policy and planning process in India remains focused on disparities at aggregate levels like the district; a recognition of how these aggregate plans translate to neighbourhood-level outcomes is essential to understanding whether these policies are achieving their objectives.
The researchers started by documenting residential segregation (neighbourhoods with >80% Muslims or Scheduled Castes inhabitants) in rural and urban areas.
Urban places are about as segregated as rural places, for Scheduled Castes. For Muslims, segregation is worse in cities.
Paul Novosad (via Twitter)
This was followed by studying the distribution of public services across marginalized and non-marginalized groups.
A 100% Muslim neighbourhood is only half as likely to have a secondary school as a neighbourhood with no Muslims…When we look at SCs, moderate SC neighbourhoods are doing ok, but the most segregated neighbourhoods again are less likely to have secondary schools.
Paul Novosad (via Twitter)
…compared with a 0% Muslim neighbourhood, a 100% Muslim neighbourhood in the same city is 10% less likely to have piped water infrastructure and only half as likely to have a secondary school.
As stated in the paper
The study of the availability of public services in segregated and integrated neighbourhoods was followed by studying the educational outcomes of young men and women who live in MG (Marginalized groups) neighbourhoods, providing suggestive evidence on the impacts of residential segregation.
Undertaken by Sam Asher, Kritarth Jha, Paul Novosad, Anjali Adukia, and Brandon Tan, the study, which comprised a database covering 75% of India’s population, is a first-of-its-kind documentation- focusing on a comparison of SC, Muslim and integrated neighbourhoods within the same city. The documentation has revealed the disparity in these neighbourhoods- such as the compromise on education.
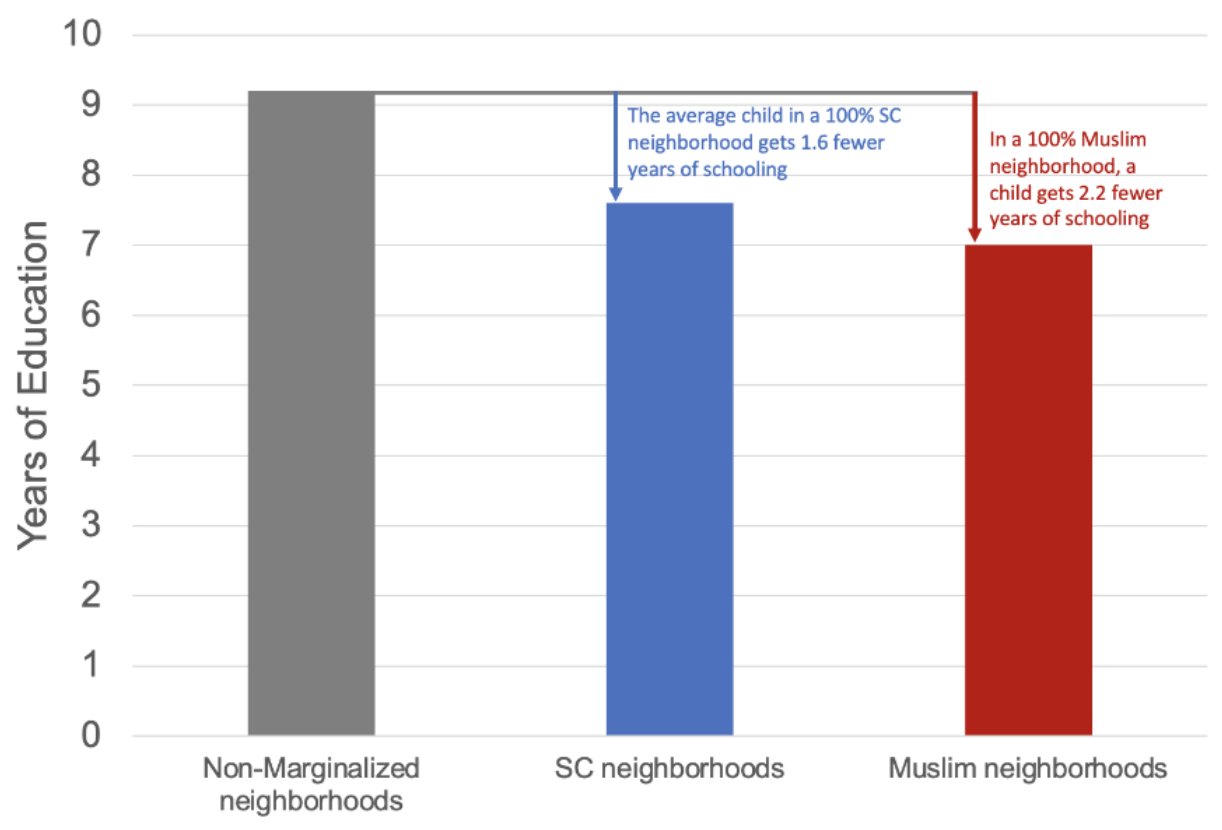
Young people have over a full year less education in fully segregated SC and Muslim neighbourhoods.
Paul Novosad (via Twitter)
Primary Results from the Study
India’s cities have a high level of segregation on the basis of both caste and religion—about as much as current levels of Black/White segregation in the United States.
Government-supplied public services are less likely to be found in neighborhoods with high numbers of SCs and Muslims.
Children growing up in SC and Muslim neighborhoods fare worse than children in non-marginalized neighborhoods in the same cities (stands true even for non-SC non-Muslim children growing up in SC and Muslim neighborhoods).
The study is based on data collected from 2011–13. Since the study is based in urban areas, it currently does not include Scheduled Tribes- of which only 4% reside in cities. Due to the lack of the availability of data focussing on predominantly OBC neighbourhoods, the paper also does not touch upon OBCs. The full paper, released by one of its authors- Paul Novosad, can be accessed below. On Paul’s Twitter handle, linking to the paper on his website, he mentions that the current draft is a work in progress and that the final paper shall be released in the near future.
The paper is authored by: Sam Asher, Associate Professor of Economics at Imperial College, London | Kritarth Jha, Development Data Lab | Paul Novosad, Associate Professor of Economics at Dartmouth | Anjali Adukia, Assistant Professor at University of Chicago | Brandon Tan, Economist at the International Monetary Fund












